Sag事故の原因
-
[自然的要因]
- Lightning Strikes
- Mountain Fire
- Snowstorms
- Line Faults
- Overgrown Vegetation
- Flash Over
- Animals
[人為的要因]
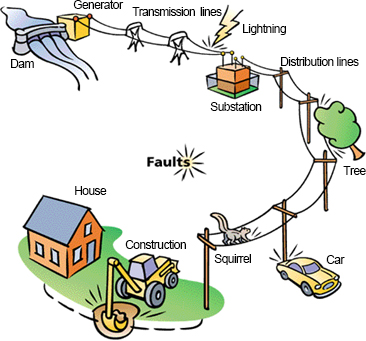
電力供給系統設備の故障
- 送電線への落雷などによって故障した場合、
遮断機を開放して故障設備を分離する間に瞬
間電圧低下が発生
- 電力系統の地絡及び短絡事故が発生すると、
事故点が分離する間に瞬間電圧低下及び瞬間
停電が発生
容量負荷の起動
- 大容量負荷起動時のPeak電流によっ
て瞬時電圧低下現象が発生
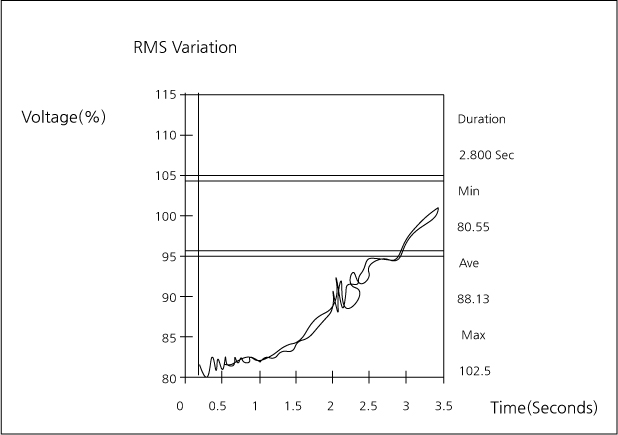
- 落雷発生地から150km以内の瞬間電圧降下率(%)
- 落雷によるSag発生
電力系統を構成する送電線が落雷などによって故障した場合、設備の損傷を最小化するために、また は電圧、電力の変動を最小限に抑えて電力系統の安定度を維持するために高速道路の故障設備を検出 し、系統から分離する必要がある。
故障点は、送電線などの各設備に設けた保護継電器で検出し、保護対象設備が故障したと判断した場合 は、遮断器を開放して故障設備を分離する。このように故障を解決する間に瞬間電圧低下が発生する。
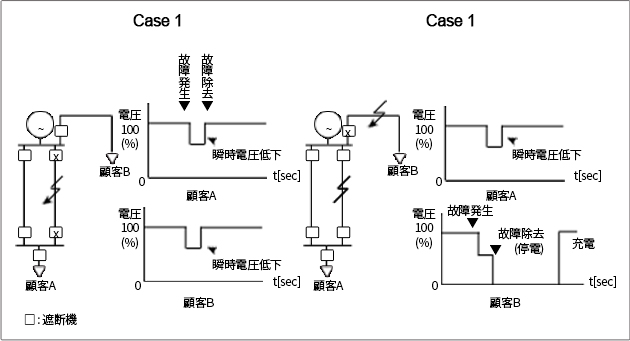
- 地絡、短絡によるSag発生
電力系統に1線地絡事故、2線地絡及び短絡、3相短絡事故が発生すると、事故点が分離されて故障が 取り除かれる間に瞬時電圧低下(Voltage Sag)及び瞬間停電(Interruption)が発生する。下の図の ように、送電線路に事故が発生した場合、A·B遮断機が動作して事故点が分離される間Voltage Sag が発生する。
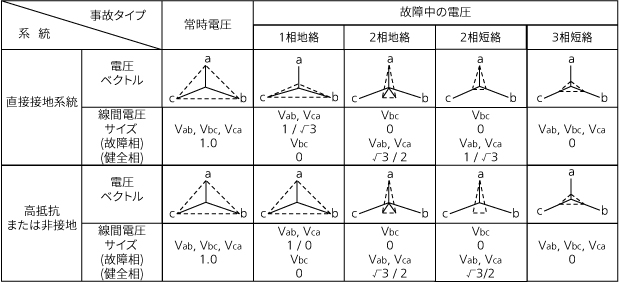
系統の事故タイプ別の電圧低下は、中性点接地方式によって異なり、1線地絡時の電圧低下の度合いは、 非接地及び高抵抗接地系統では少なく、直接接地系統では大きくなり、2相地絡及び3相地絡時の電圧低 下の度合いは系統接地方式に関係なく大きくなる。
[このような系統事故による電圧低下の差を電圧ベクトルで表すと、次のようになる。]
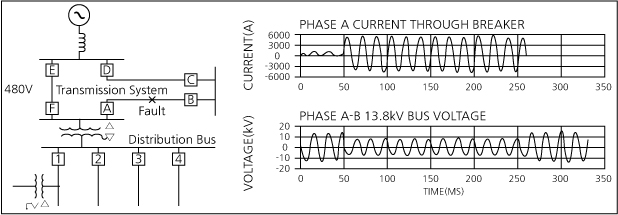
- 大容量モータ起動によるSag発生
電力設備の大型化につれ、電動機の容量も大型化され、起動時に発生する起動電流によってVoltage Sagが発生する。
- 落雷による韓国電力の送·変電設備の再-閉路(Re-Closing Circuit)動作によ る瞬間電圧降下発生経路
